Every year, there are new medical breakthroughs that change the face of healthcare. With all the...
16 Jaw-Dropping Medical Technology Statistics of 2022
Technology has come a long way since the first iPhone was released in 2007; these medical technology statistics confirm that it’s advancing at an exponential rate and starting to take over our lives.
Today, doctors can use technology to diagnose patients without ever seeing them face-to-face. Hospitals use robots to deliver meal trays and medication, while surgeons use robotic arms to operate on patients from across the room.
Soon enough, we may be able to 3D print organs for surgery instead of relying on donors who might not match your blood type or tissue type.
As these technologies continue to develop, practices must stay up-to-date with what’s happening. This article highlights 16 shocking medical technology statistics in 2021. If you’re wondering how they may affect your life as a physician or patient, this will hopefully help answer some of your questions.
What are the latest trends in healthcare?
Nowadays, healthcare can be tough and confusing for patients. There are always new treatments coming out and figuring out what’s best can seem like a daunting task. However, we’ve explored some of the latest trends in healthcare and they are pretty exciting.
For example, has a patient ever told you that they feel guilty if their wearables show a low step count and so immediately go for a walk? Simple wearable devices that monitor patients’ heart rate and step count have the potential to save lives. Studies show that 10% of people who wear such devices have improved their lifestyle as a result of the data. Prescribing a Fitbit to your patient could expand their lifespan.
Technology in medicine is evolving at an incredible speed and doctors are now able to carry out procedures that were once unthinkable. From new and innovative surgical techniques to ingenious new equipment, healthcare has improved immensely; and the medical technology statistics that come with it continue to astound.
What are the best medical technology statistics in 2021?
Every year, new discoveries and inventions revolutionize healthcare. We gathered 15 of the most surprising and innovative medical technology statistics from 2021.

1. Computer algorithms are now able to diagnose patients
After the shocking realization that 12 million people per year left their doctor’s office with a potentially harmful misdiagnosis, many doctors turned to technology to help improve their diagnostic accuracy. Today, Tencent, a Chinese IT enterprise, has developed an AI (Artificial Intelligence) that can effectively diagnose diseases. This includes several different types of cancer.
This type of new medical technology is becoming more and more popular in hospitals. Statistics show that 80% of hospitals and medical practices plan on, or already have, some kind of AI application in place. Doctors believe this will be crucial in the future. And with the accuracy of AI cancer diagnostics topping 90%, it certainly looks that way.
2. Over 10 million mobile health apps available for download worldwide
In 2021, it is estimated that there will be more than 10 million apps available globally to help patients lead a healthier lifestyle.
Providing medical solutions through mobile apps is an increasingly popular trend in 2021. With the average Millennial spending 5.7 hours on their phones per day (and a shocking 13% spending over 12 hours), it makes sense to let your smartphone judge whether you’re leading a healthy lifestyle.
There are over 400,000 healthcare apps available for download in app stores and more than 200 are being added each day. This ranges from general wellness apps to calorie counters, at-home workouts to sleep trackers.
The number of apps dedicated to specific conditions is becoming more common. This market now represents 40% of all health-related apps.
Even though 66% of US hospitals already have apps available, only 2% of their patients are active on them. Despite the fact that a whopping 80% of patients say that they would like to use their smartphones more to interact with healthcare providers, hospitals seem to struggle with digital engagement.
The lack of app use could be an issue with the app’s usability or just a case of making patients more aware. However, healthcare apps are one of the medical technology trends that practices need to get on board with in 2021.
3. The global mobile health app market is expected to reach US$102.35 billion by 2023
The total global market for healthcare apps was valued at just $2.4 billion in 2017. In 2020, it had already risen dramatically to $40.05 billion. Experts predict that this will continue to rise by 17.7% from 2021 to 2028. If this trend continues, the market could be worth a staggering $125.32 billion in 2028.
The benefit of improving patient care and patient experience are the main contributing factors to this increase. The impacts of COVID-19 have also caused this number to rise with remote doctor’s appointments, patient monitoring, and telehealth.
The popularity of healthcare apps is also boosted by the growth percentage of smartphone users which has risen from 1.86 billion in 2015 to over 3 billion today. This growth is expected to continue and surpass 4 billion by 2023 which will further increase healthcare app usage in the world.
4. By 2025, one in every 3 adults in America will wear a fitness tracker
The latest medical technology statistics show that 1 in 5 Americans currently wear a fitness tracker such as Fitbit or a smartwatch. This is also predicted to grow by a further 20% between now and 2025.

A few other interesting factors are that women are more likely to wear a fitness tracker than men (25% vs. 18%), Hispanic adults are more likely to wear one than whites (26% vs. 20%), and people in households earning more than $75000 per year are more likely to wear a fitness tracker regularly.
Furthermore, 28% of China’s population uses a connected health device – this is the highest number of any country in the world.
5. The use of telehealth has increased by over 50% since the start of 2020
Telehealth is way up from just 18% in 2018 and comes as no surprise as COVID-19 forced many medical practices to implement a remote option.
On one hand, regular medical appointments were severely impacted by the pandemic, and medical practices scheduled 63% fewer face-to-face check-ups as coronavirus emerged.
Telehealth appointments, on the other hand, shot up by 154% during the first week of March 2020. It looks as though telehealth may be here to stay.
74% of US consumers would use a telehealth service and 76% say that access to medical treatment is more important to them than human interaction. This also includes over 65’s as almost 60% stated that they’d be willing to manage a long-term condition virtually.
Furthermore, adopting telehealth could save the US healthcare industry a whopping $1,500 per visit and could save patients an average of 3 hours each time they need to see a doctor. By 2026, it’s estimated that the telehealth market will reach a staggering $186.5 billion.
6. 68% of patients say they’re more likely to choose medical providers that offer the ability to book, change, or cancel appointments online
New medical technology is becoming more and more popular, especially among Millennials and Gen Xers. Now, 68% of all patients expect to be able to book medical appointments online – this is up 17.2% from 2016. In fact, over half said they’d switch practices for the ability to book appointments online.
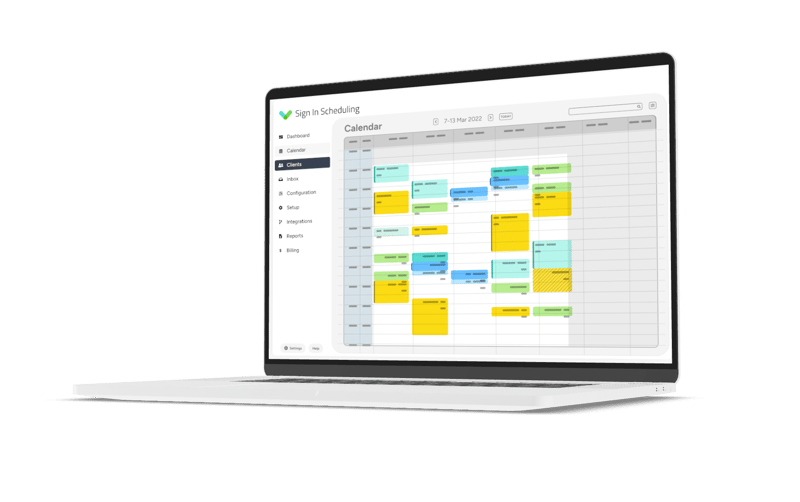
So, what’s causing this? Well, 35% of online medical appointments were booked outside of the typical 8 am – 5 pm timeframe and only 50% of people that phoned their doctor for an appointment were able to book the first time. The other half had to call back later. This is one of the many issues that online booking eliminates.
So, as far as convenience and ease of booking go, online appointment scheduling is well and truly in the lead.
7. The global medical devices market in 2020 was valued at $442.5 billion
The medical devices industry was worth a whopping $442.5 billion in 2020.
This figure is the result of an increased number of healthcare units being opened up across the globe, an increase of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) and ventilators manufactured to combat COVID, and a higher need and level of medical technological advancements. It’s a growth of 4.4% since 2015.
Strangely enough, COVID has also caused a slight dip in the medical devices market. Local US lockdowns caused the value to drop from $456.9 billion in 2019 to $442.5 billion in 2020 as restrictions hindered the supply chain. But, this number is expected to completely recover and experts predict that the industry will be worth $603.5 billion by 2023.
8. The surgical robot market is expected to reach over $24 billion by 2025
Back in 2018, the global robotic surgery market was valued at $5.5 billion. However, technological advancements in the field have skyrocketed the use of robots in hospitals since then and by 2025, the industry’s value is predicted to grow by 24.4% to a shocking over $24 billion.
One of the most impressive medical technology statistics, robots are mainly used for minimally invasive surgery. But, the growth of the industry will soon make many more types of operation possible, including Neurosurgery, Orthopedic surgery, and Gynecology surgery.
9. Artificial intelligence can now be used to detect pandemics
Artificial Intelligence is one of the top emerging medical innovations in the world, however, coronavirus caused a recent shift in priorities. They are now being developed to help combat global infectious diseases and prevent a catastrophe like COVID hitting us this hard in the future.
The new type of technology is a machine learning algorithm that tracks trends in data that detect new outbreaks of disease. It analyzes and predicts the spread of disease, the infection rate, and the infection trend, and then provides an early warning or alert.
This data is so advanced that, Canadian artificial intelligence BlueDot, actually predicted the coronavirus pandemic before the WHO even notified the public.
10. IoMT market will soon be worth $142.45 billion
The internet of medicine is growing. It’s predicted that the IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) market will be worth $142.45 billion by 2026.
These days, everyone wants data, statistics, and real-time analysis. Companies like Deloitte and MedTech are using this to their advantage.
The Internet of Medical Things describes physical objects embedded with sensors, trackers, or other technologies with the ability to connect to the internet.

The predicted growth rate of the IoMT is 28.9% from 2021, surpassing a shocking $142 billion by 2026. This is partly on account of preventing chronic diseases and worldwide pandemics.
Nevertheless, it has the potential to lower the price of operational and clinical wastefulness by $100 billion per year. More than half of physicians (64%) believe it can help make things easier for medical staff.
The overall IoT (Internet of Things) is expected to grow to a whopping $1319.08 billion by 2026. This means the medical industry will make up over 10% of the total IoT market.
11. Facial recognition – even with a facemask on
Facemasks have become a thing of the norm since 2020. However, with the public now concealing more than half their face, there were initial concerns about how this would affect security.
But thanks to the Japanese security company NEC, a camera system has been developed that can identify people even when they are wearing a face mask.
The camera focuses on exposed facial features, such as people’s eyes, to pinpoint their identity. It can identify people in milliseconds with a 90% accuracy rate and even works in large crowds.
Before the pandemic, up to 50% of cameras failed to identify people wearing masks, so this is a dramatic and much-needed improvement. NEC cameras are now used by both police and airport security systems.
12. XR devices to reach over $4 billion
By 2025, the use of XR (Extended Reality) devices is expected to reach over $4 billion. This includes Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) too.
The use of Extended Reality is an emerging technology and a growing trend in the medical industry. These technologies have many uses from training new medical professionals to surgical simulations, diagnostic imaging, and patient care.
By 2025, the market for Extended Reality devices is predicted to rise by 31.63% and be worth $4,057.144 million.
13. Global funding for Nanotechnology to exceed $125 billion
Nanotechnology is the use of atomic or molecular matter at the nanoscale.

The medical industry is currently using nanoparticles and manufactured nano-robots to conduct cellular repairs. This could potentially be used to kill bacteria, deliver drugs to the body, detect foreign cells in the bloodstream (such as cancer cells), and repair cells that are damaged.
This type of technology has been around since 1991 and medical technology statistics show that it has been steadily developing since then. Experts predict that the industry will be worth over $125 billion by 2024 and it has the power to revolutionize healthcare.
14. Pagers and other outdated communication systems cost hospitals $8.3 billion annually
Pagers contribute heavily to lost productivity and increased patient discharge times which consequently costs hospitals over $8 billion annually in revenue. This seems even more surprising when you consider that over 80% of hospitals still use such outdated technologies.
However, there are some very simple reasons that doctors still use pagers:
- Because of medical equipment like X-Ray machines, some walls are specifically built to stop signals from getting through – hence the abundance of mobile phone dead zones in hospitals.
- To get mobile phones to work reliably in hospitals, they would have to invest in service boosters. But, the industrial-level products can cost thousands of dollars each.
- Pagers can easily send a message to hundreds of people at once.
- Pagers only need to be charged once a week (or sometimes last even longer than that), which is much easier to manage than mobile phones that require daily charging.
So, despite the pagers being rather clunky and unattractive, pagers do prove useful to medical staff. Nevertheless, the slight downside of only being able to send a message and not reply to them had prompted some hospitals to consider moving towards a more modern form of communication such as secure, HIPAA-compliant messaging apps.
15. Alexa might now be able to diagnose your cold
Voice search is an increasingly popular use of finding information. Inspired by voice search, a start-up company called Vocalis Health asked people to donate their voices to help them create an app to diagnose diseases.

The Israeli-US company has built a smartphone app that can detect flare-ups by noticing changes in your voice. It can be used to detect something as simple as a common cold or even detect COVID-19 by checking for other symptoms like shortness of breath.
The app is not designed to provide a definite diagnosis. However, it can help clinics trace cases and identify who might need to be tested, isolated, or need urgent medical care.
Alexa can also now be used to detect things outside of physical illness like emotional stress, a person’s location by the background noise, and the accent, age, or gender of the speaker. This is another excellent example of machine learning algorithms revolutionizing new medical technology.
16. Drones can be used to collect blood samples from those in rural areas
If living in a rural or isolated area has made it difficult for you to access healthcare, then things may be about to change.
Drones are now being used in some of the more remote areas of the UK (including Scotland’s Outer Hebrides) to deliver coronavirus tests and collect blood samples from those living there.
Controlled via QR code and camera, the drones can travel at speeds of up to 100 mph and turn tests around in as little as 2 hours (compared to the 2 days it would take via ferry). There are reports of remote patients getting results quicker than those living in big cities.
It’s not just the UK that’s using this kind of technology. Drones have also been utilized in the US to carry blood over the Arizona desert. The medical technology statistics for these drones are off the charts as the drone managed to keep the blood cold for the duration of the 160-mile journey and dramatically beat the time achieved by a vehicle.
In the future, experts expect this technology to spread over the rest of the world, allowing remote regions to access better medical care and potentially saving more lives.




Blog comments